








A FINE AND HOROLOGICALLY SIGNIFICANT JAMES I FIRST PERIOD LANTERN CLOCKWILLIAM BOWYER
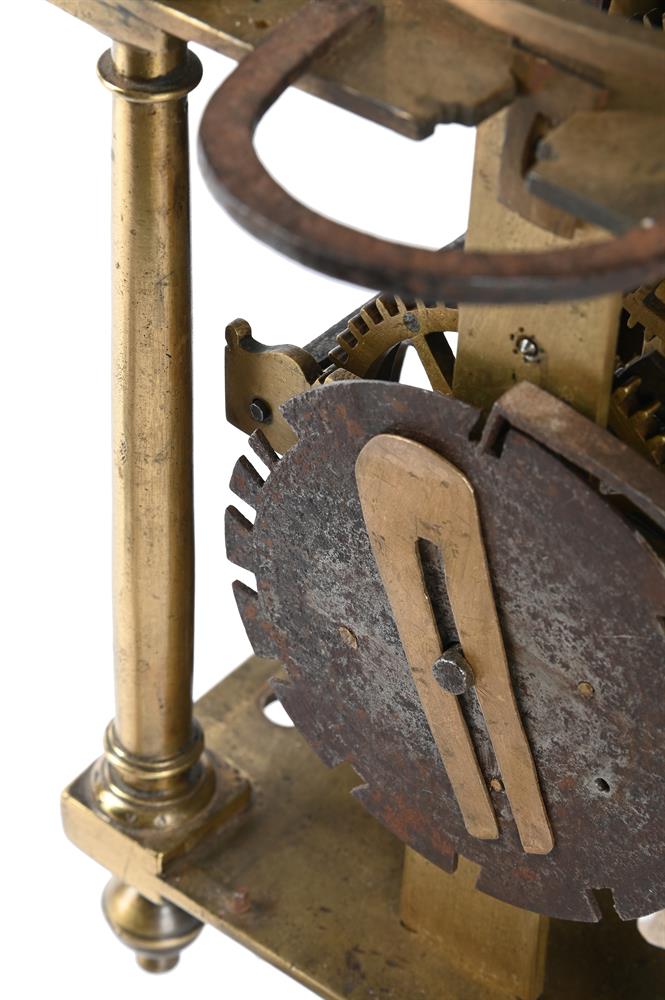
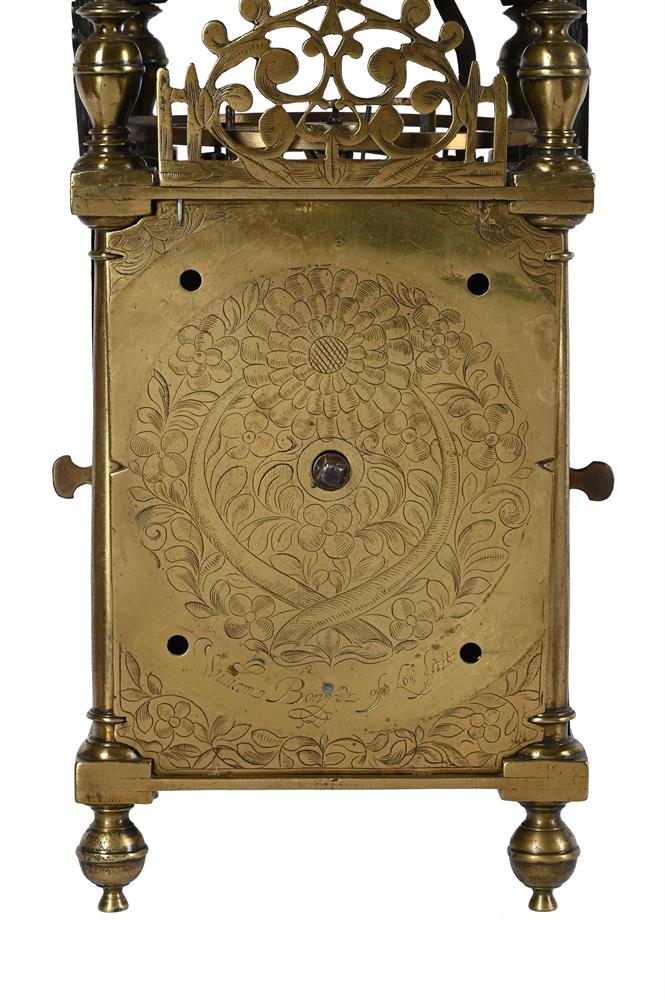
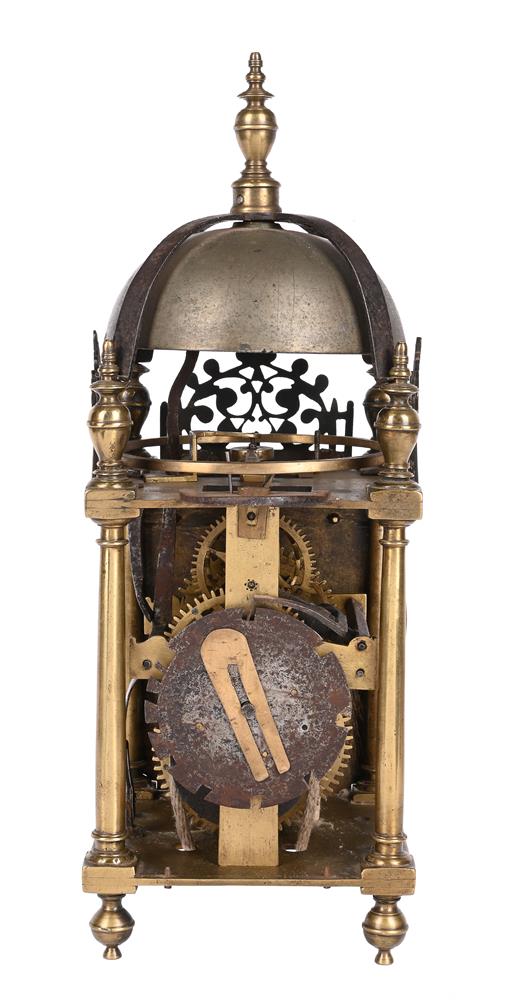
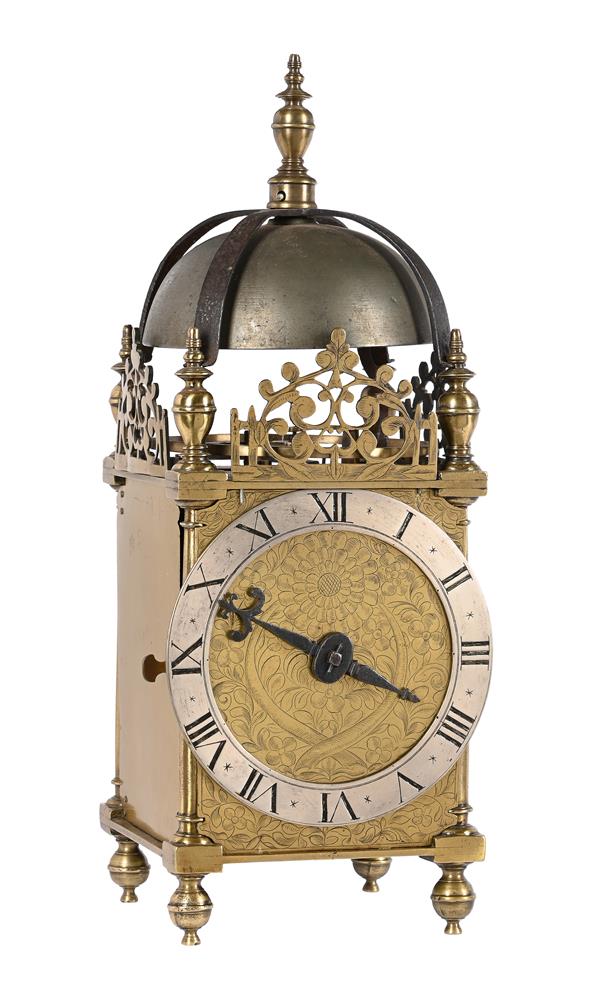
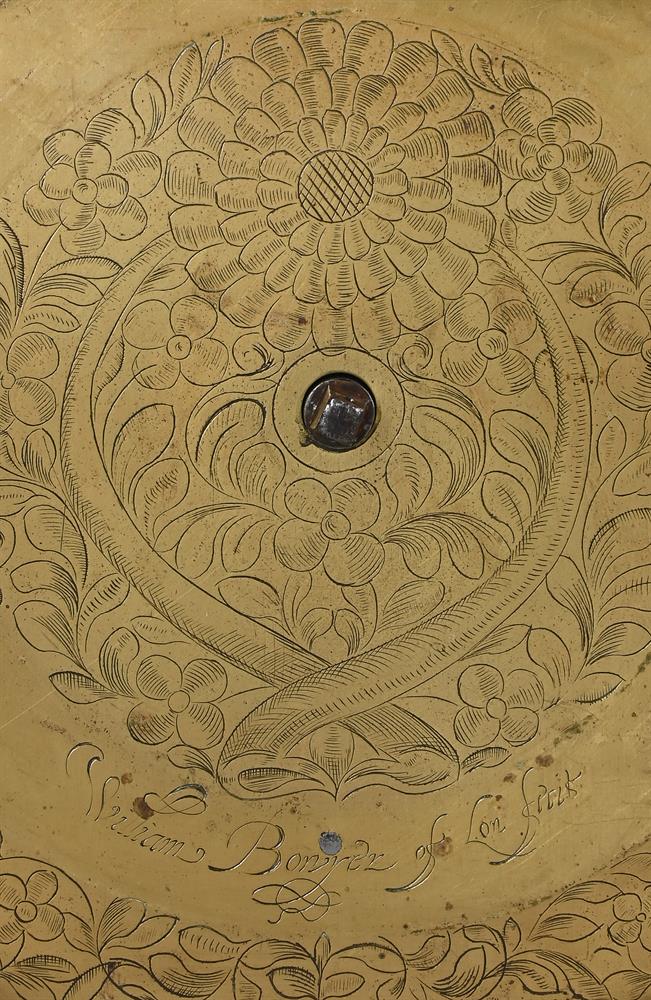
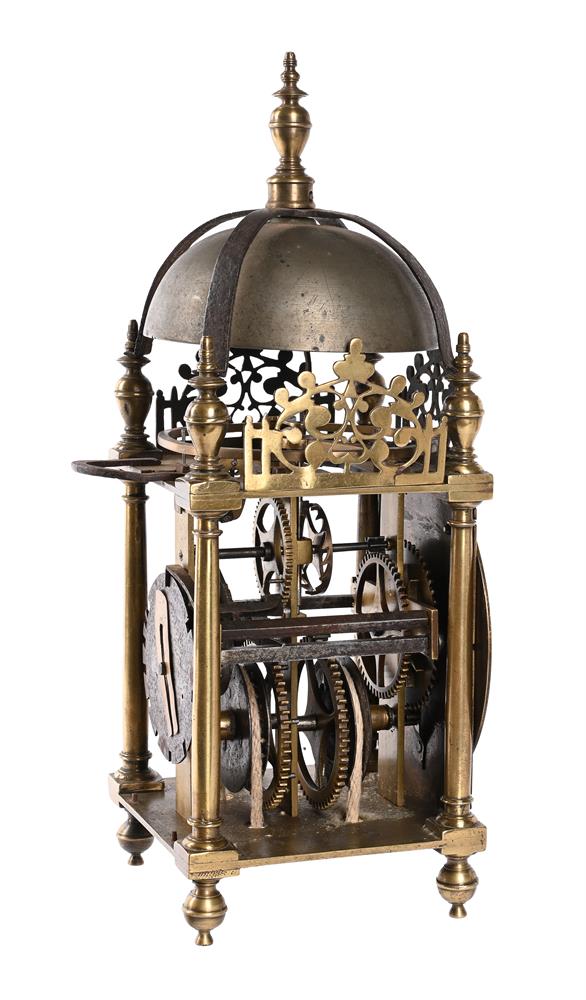
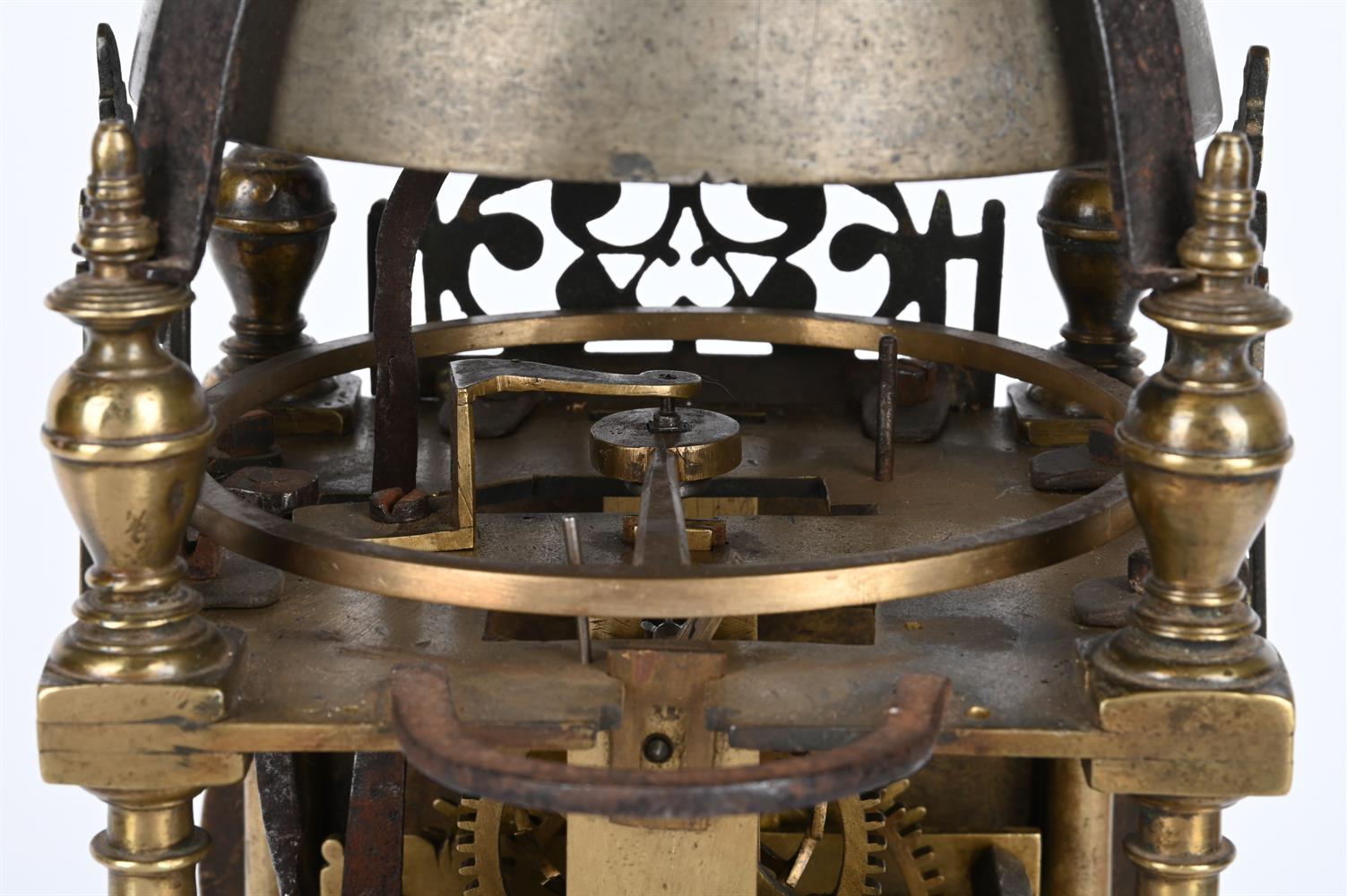
A FINE AND HOROLOGICALLY SIGNIFICANT JAMES I 'FIRST PERIOD' LANTERN CLOCKWILLIAM BOWYER, LONDON, CIRCA 1620The separately wound trains with iron-cheeked pulleys to the great wheels, the going train with reinstated verge escapement regulated by horizontal balance oscillating above the frame top plate, the strike train sounding the hours on a lugged bell mounted above the frame via an iron countwheel with overlift provided by an iron-walled hoop wheel cut with a single slot, the dial finely engraved with a large chrysanthemum bloom over twin entwined stalks set within a field of scrolling flowering foliage to centre, within applied narrow silvered Roman numeral chapter ring incorporating floating asterisk half hour markers and concealing fine signature William Bowyer of Lon Fecit engraved in a downward curve to the plate behind the lower part, with fine sculpted steel hand and foliate engraved infill matching that of the centre occupying the upper quadrants and the lower margin, the frame with finely turned generous Doric column corner posts beneath distinctive ovoid vase finials with banded waists, the front and sides applied with symmetrical scroll pierced cast brass frets with the front incorporating foliate engraved detail, beneath domed iron bell bearer capped with a conforming vase finial incorporating pinned plinth upstand for securing the lugged bell, with brass side doors and the rear with iron hanging hoop over spurs applied to the brass backplate, on collar-turned ball feet.40cm (15.75ins) high, 15cm (6ins) wide, 18.5cm (7.25ins) deep.William Bowyer is recorded in Loomes, Brian Clockmakers of Britain 1286-1700 as the son of Ralph Bowyer (yeoman of Warfield Berkshire) who is believed to have been married to Alice Mansworth in 1590. William was probably born around this time and by 1616 was a member of the Pewterers' Company when he took-in Thomas Taylor (son of Ralph Taylor, a milliner from Halesowen, Shropshire) as an apprentice. Bowyer took-in no less than five further apprentices prior to the formation of the Clockmakers' Company in 1631, including John Pennock (son of William Pennock of Guisborough, Yorkshire) in 1620. Although he subscribed £5 towards its charter and was made free of the City in 1630, William Bowyer did not apparently join the Worshipful Company on its establishment the following year.Bowyer is thought to have been first married to Margery Barlow of Litchfield, Staffordshire, however, by 1631 he was married to Prudence with whom he had five children (three of which sadly died in infancy). By 1638 Bowyer was living in the parish of St. Andrew Undershaft, he took-in Joseph Jackson (through Thomas Dawson) as apprentice that year and during the following decade took-on at least four more, this time through the Clockmakers' Company. One of these apprentices was Nathanial Allen (probably around 1641/2); Allen subsequently married a Phillipa Bowyer in 1646 hence became related to William through marriage.In 1640 William Bowyer was invited to become an Assistant of the Clockmakers' Company, however it appears that he was reluctant to serve the Company as in July 1642 he gave 'a great chamber clock' in return for excusal from any further duties. Nevertheless he became an Assistant in 1651 and a Warden in 1653 the year of his death.The present clock belongs to a group of less than half-a-dozen surviving particularly early examples made by Bowyer either just before or around 1620. Of the others the first (dated 1617) was sold at Bonhams, London sale of Fine Clocks 11th July 2018 (lot 60 for £43,750) and the second is illustrated in Loomes, Brian LANTERN CLOCKS & Their Makers on page 79 (Figures 7.1-4). Another is illustrated in White, George English Lantern Clocks onpage 101 (Figure II/125 showing movement only), and possibly a fourth on page 113 (Figure II/145).All of the above examples share the same frame castings which are very closely related to those used by the earliest of English Lantern clock makers, brothers Robert and Thomas Harvey. These frames are characterised by having well-proportioned Doric column corner posts surmounted by slightly shouldered ovoid vase finials each decorated with a ring around the waist beneath a disc knop. The ball feet are also cast with a collar matching that of the finials. Indeed when the frame of the present clock is compared with that of an example by Thomas Harvey illustrated in Loomes, Brian LANTERN CLOCKS & Their Makers it can be seen that the castings differ only in very slight detail.In addition to sharing the same design of frame castings it has been noted by Brian Loomes in his article William Bowyer, an exciting and important discovery published in 'Clocks' magazine, June 2018 (pages 9-12) that the movement pivot bar castings follow the same form as those used by Robert and Thomas Harvey. This suggests that these castings may have a common source, most likely the Harvey workshop. It is therefore likely that, during his formative years, William Bowyer had some form of connection with this very important workshop. From the images available it can be seen (with the possible exception of the last clock illustrated by White on page 113) that this group of clocks are all essentially identical with regards to the layout and detailing of the movements. All have iron countwheels, iron-walled hoopwheels, straight hammer checks and iron cheeks to the pulleys (where the originals survive). They also share the same frets hence only essentially differ in the treatment of the dials, and whether an alarm was originally fitted. These inherent similarities suggest, that even at this very early date, a degree of standardisation was being adopted mostly through the use of common castings.The present clock is noticeably well finished with each of the cruciform movement pivot bars having decorative scroll-shaped detailing just above the hammer arbor pivots. This attention to detail is carried forward to the dial which exhibits fine albeit unusual foliate decoration to the entirety of the dial centre. It is perhaps interesting to compare this decoration with that of Bowyers celebrated 'Memento Mori' great chamber clock of 1623 illustrated in Bruce, W.F. EARLY ENGLISH LANTERN CLOCKS 1600-1700 (2013) on page 17. Although the decoration of this larger clock lacks a large flowerhead (or any other large single element) the foliate infill has a similar feel to that of the present clock, albeit in a perhaps slightly more developed form incorporating scrolls and loops to the design.Please see the page-turning catalogue to continue reading the final part of this footnote.
- The cost is converted to USD at the rate of 1 GBP = 1.1935 USD on 2023-03-07.
-
Sign in to view
Lot number
-
Sign in to view
Estimate
-
2023-03-07
Sale date
-
Sign in to view
Realised price
-
Sign in to view
Opening price
-
Sign in to view
House name
-
Sign in to view
Auction sale name
-
Sign in to view
Country
-
Categories
Sign in to view -
Tags
Sign in to view